What Is Optical Character Recognition and How It Works
So, what exactly is Optical Character Recognition, or OCR? At its simplest, it's technology that teaches a computer how to read. It takes images—like a scanned contract, a photo of a receipt, or a PDF—and converts the text within them into fully editable and searchable digital data.
Think of it as a bridge between the physical and digital worlds. It sees the letters and numbers in a picture and "types" them out for you, but at lightning speed.
From Image to Editable Text
Before a technology like OCR came along, a scanned document was just a flat picture. Sure, you could see the words, but to your computer, they were just a meaningless collection of pixels. You couldn't copy a paragraph, search for a client's name, or pull a number into a spreadsheet. The only option was to sit there and manually type everything out. We all know how slow, tedious, and error-prone that is.

This is where the magic happens. OCR completely changes the game. It scans that flat image, recognizes the shapes of each letter and number, and converts them into actual text your computer understands.
The Power of Digital Conversion
Suddenly, that static image becomes intelligent. That scanned invoice is no longer just a picture; it's a dynamic source of data that can be automatically sorted and entered into your accounting software. A quick photo of a business card can instantly become a new contact in your phone, no typing required.
This isn't simple stuff, either. The software uses a sophisticated mix of pattern recognition and artificial intelligence. It's been trained on millions of documents to learn the difference between an 'O' and a '0', or an 'l' and a '1', across countless fonts and even messy handwriting.
By automating text extraction, OCR wipes out the most mind-numbing part of data entry. This lets businesses process information faster, slash operational costs, and sidestep costly human errors.
Ultimately, OCR is a cornerstone of modern business automation. It turns those daunting piles of paper and folders of image files into what they should be: valuable, accessible, and actionable digital information.
Core Benefits of OCR at a Glance
To really bring it home, let's look at the direct impact OCR can have on any workflow. The advantages go far beyond just saving a few minutes of typing.
| Benefit | Impact on Business | Real-World Example |
|---|---|---|
| Time Savings | Slashes manual data entry time, freeing up your team for more important work. | An accounting clerk processes 100 invoices in an hour, not an entire day. |
| Increased Accuracy | Drastically reduces the human errors that come with retyping information. | A hospital digitizes a patient's medical history without dangerous typos. |
| Enhanced Searchability | Turns your entire document archive into a private, searchable database. | A legal team instantly finds a specific clause across thousands of scanned contracts. |
As you can see, implementing OCR isn't just about convenience—it's about creating a more efficient, accurate, and intelligent business.
The Surprising History of OCR Technology
You might think Optical Character Recognition is a product of the modern digital age, but its story actually begins more than a century ago—way before the first personal computers were even a dream. The quest to teach machines how to read didn't start with software, but with some seriously clever engineering aimed at solving a very different kind of problem.
The journey kicks off not in a tech hub, but with a physicist named Emanuel Goldberg. Back in 1914, he invented a remarkable device that could read characters and convert them into standard telegraph code. This was, in essence, one of the very first forms of OCR, and it set the stage for everything that came after. The early days of OCR are full of these fascinating origins.
From there, the technology slowly but surely evolved, pushed forward by the growing needs of businesses and government agencies.
From Telegraphs to Mainframes
The next big jump happened in the 1950s, when IBM officially gave the technology its name: "Optical Character Recognition." At the time, companies were practically drowning in paperwork. The first commercial OCR systems were built to rescue them, automating data entry for massive corporations and even postal services.
These early machines were huge, clunky, and could only read a handful of specific fonts. They were a world away from the slick software we have today, but they proved a crucial point: automated document reading wasn't just possible, it was incredibly valuable. This era laid down the fundamental principles of scanning and character analysis that are still in use.
The AI Revolution
What really kicked OCR into high gear was the rise of artificial intelligence and machine learning. As computers got faster and algorithms grew smarter, OCR software began to do more than just match patterns—it started to learn.
Instead of being stuck with a few pre-approved fonts, modern OCR can now tackle incredible challenges. It can:
- Recognize thousands of fonts: From your standard Times New Roman to handwritten script.
- Understand complex layouts: It knows the difference between columns, tables, and images on a page.
- Clean up messy images: The software can automatically correct for tilted pages, blurry text, and bad lighting.
The real game-changer was AI. It turned OCR from a simple tool that matched shapes into an intelligent system that understands context. This is the magic that makes instant document scanning on your phone possible.
This long history shows that OCR isn't just some new trend; it's a mature, dependable technology built on decades of innovation. Every step of the journey, from Goldberg's mechanical reader to today's AI-powered platforms, has made it more accurate, accessible, and vital for running a business. The tools we take for granted today are standing on the shoulders of some pretty impressive giants.
How an OCR System Reads a Document
Ever wonder what actually happens when you scan a document and the text magically becomes editable? It’s not a single, instantaneous event. Think of it more like a meticulous digital assembly line, where a raw image gets transformed, piece by piece, into structured, usable information.
This process is remarkably consistent, whether you're snapping a photo of a single receipt or feeding a batch of a thousand invoices into a system. It can be broken down into three key stages: getting the image ready, figuring out the characters, and then cleaning up the results. Let's walk through it.
This quick visual breaks down the core journey from a simple picture to clean, digital data.
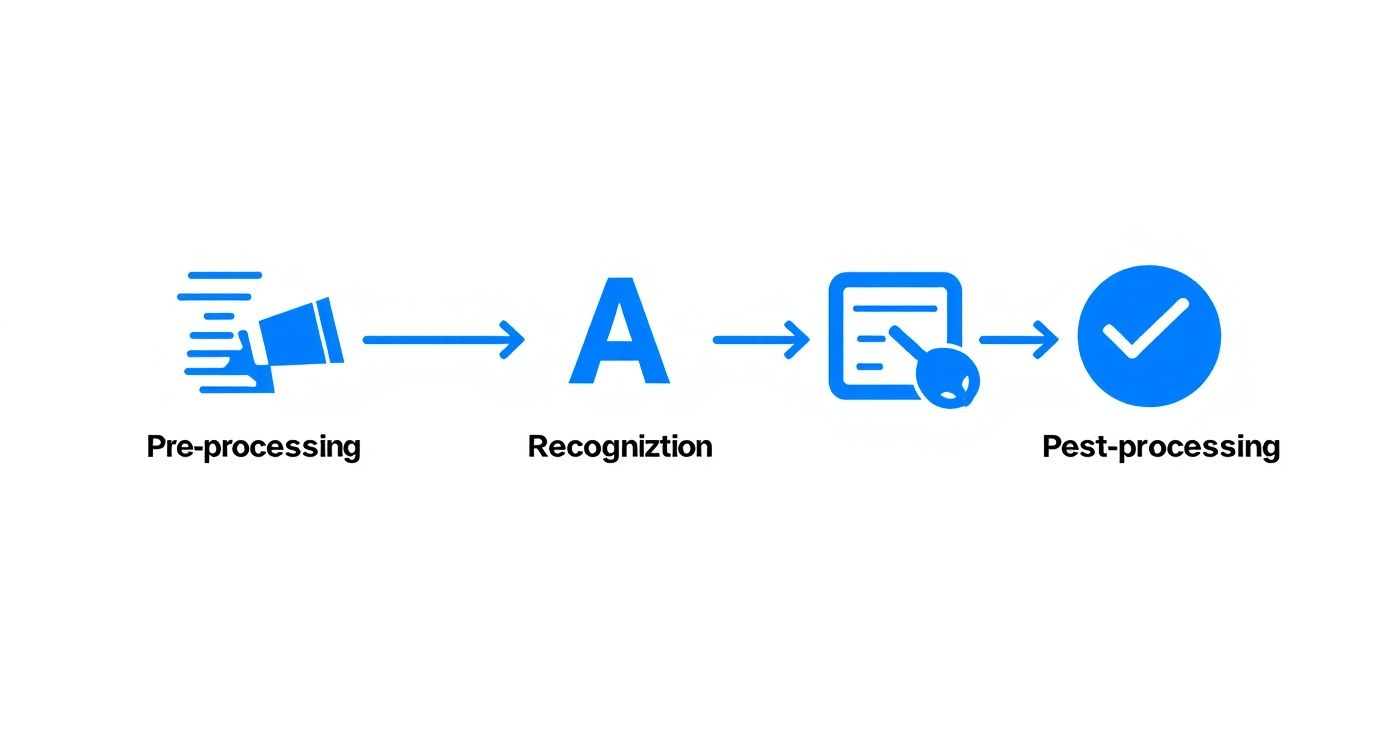
Each step builds on the last, all with the goal of getting the most accurate output possible.
Step 1: Image Preprocessing
Before any software can "read," it needs a clean slate. The first step, called preprocessing, is all about tidying up the image to make it as clear as possible for the OCR engine. It’s like wiping a dusty pair of glasses before you try to read a book.
This stage involves a few crucial automated tweaks:
- Deskewing: The software finds and corrects any tilt in the scanned document, digitally straightening it out. No more crooked pages.
- Binarization: It converts the image to a simple black-and-white format. This makes the text stand out sharply from the background, removing distracting colors and shadows.
- Noise Removal: This function acts like a digital dust buster, getting rid of stray specks, smudges, or pixelated artifacts that aren't part of the actual text.
Without a solid preprocessing step, even the smartest OCR engine would trip up on a messy scan. Getting this right is fundamental to the final accuracy.
Step 2: Character Recognition
Now that we have a pristine image, the real magic begins. This is where the OCR software starts acting like a digital detective, scrutinizing every shape on the page to identify individual letters, numbers, and symbols. The system has been trained on a massive library of characters, so it can recognize an incredible variety of fonts and handwriting styles.
It typically uses one of two main approaches:
- Pattern Matching: This is the more straightforward method. The software compares a character's shape against a library of known fonts to find an exact match. It's highly effective for clean, standardized printed text.
- Feature Detection: A more sophisticated technique. Here, the AI breaks each character down into its fundamental components—the lines, curves, and intersections. Instead of looking for a perfect "T," it looks for a vertical line crossed by a horizontal one, making it far more flexible with unfamiliar fonts.
This recognition phase is the heart of what OCR is all about. It’s the moment a machine stops seeing a collection of pixels and starts understanding language.
Step 3: Post-Processing and Validation
The job isn't done once the characters are recognized. The final stage, post-processing, is like having a meticulous editor review the work. No OCR is 100% perfect on the first pass, so this step uses AI and language models to spot and fix common errors.
For instance, if the software misread the letter "o" as a zero and produced "invaice," a built-in dictionary would flag the mistake and correct it to "invoice." It's an essential quality control check.
This phase also involves structuring the output. Instead of spitting out a raw block of text, the system identifies what the data is—placing invoice numbers, dates, and line items into the correct fields. This turns chaotic text into organized data ready for your accounting software. For a great example of this in action, you can see how to scan documents to Excel and automate your entire workflow.
This meticulous, three-step journey is how a simple picture of a document becomes a powerful source of real, actionable data for your business.
How Businesses Are Using OCR in the Real World
Understanding the theory behind Optical Character Recognition is one thing, but seeing it in action is where you really grasp its power. Businesses across nearly every industry are using this technology to solve real-world problems, slash tedious manual work, and finally unlock the information trapped inside their paper and digital documents. It's the quiet engine driving a massive shift in automation.
From the finance department to the doctor's office, OCR isn't just a "nice-to-have" tool; it's becoming a fundamental part of how work gets done. It acts as the crucial bridge between the physical world of paper and the digital workflows that define modern business, turning static images into active, searchable data.
Automating the Financial Back Office
Nowhere is the impact of OCR more obvious than in accounting and finance. These departments have historically been buried under mountains of paper—invoices, purchase orders, expense receipts, you name it. Manually keying in data from every single document is painfully slow, expensive, and a breeding ground for human error.
OCR completely flips the script on these old processes.
- Invoice Processing: Instead of someone manually typing in vendor details, invoice numbers, and line-item amounts, OCR software pulls this information out automatically. A platform like DocParseMagic can chew through hundreds of invoices in the time it takes a person to process just a few by hand.
- Expense Reporting: Team members can just snap a picture of a receipt with their phone. OCR technology then reads the merchant name, date, and total, and populates the expense report for them. No more shoeboxes full of faded paper.
- Bank Statement Reconciliation: OCR can scan and digitize paper bank statements, allowing you to import the transaction data directly into your accounting system. This makes reconciliation faster and far more accurate.
This kind of automation frees up finance professionals to spend their time on high-value analysis and strategy instead of mind-numbing data entry. If you want to see this in more detail, it’s worth exploring how modern document data extraction software makes these powerful workflows possible for any business.
Transforming Healthcare and Legal Workflows
The applications for OCR go far beyond just accounting. In fields that handle dense, text-heavy documents, the ability to make information digital and searchable is a game-changer.
In regulated industries like healthcare and law, getting to the right information quickly isn’t just about being efficient—it's often critical for compliance and making the right call under pressure.
Hospitals and clinics, for instance, use OCR to digitize patient records, old charts, lab results, and insurance forms. This helps build a complete and searchable electronic health record (EHR), giving doctors instant access to a patient's entire medical history. In an emergency, that speed can make all the difference.
It's a similar story for legal teams, who use OCR to tackle immense volumes of case files, contracts, and discovery documents. Rather than having a paralegal manually sift through thousands of pages, a lawyer can use an OCR-powered system to search for a specific name, date, or clause across the entire case file in seconds. This saves an incredible amount of time and helps them build a stronger case.
The table below gives you a quick snapshot of how a few key industries are putting OCR to work to solve some of their biggest headaches.
OCR Applications Across Key Industries
A comparative look at how different sectors use OCR technology to overcome unique challenges.
| Industry | Common Use Case | Primary Business Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Banking & Finance | Processing checks, loan applications, and invoices. | Drastically reduced manual data entry and error rates. |
| Healthcare | Digitizing patient records and insurance claims. | Faster access to critical patient data and improved care. |
| Legal | Making contracts and case files searchable. | Massive time savings in research and e-discovery. |
| Retail | Capturing data from receipts for loyalty programs. | Enhanced customer engagement and streamlined returns. |
| Logistics | Scanning bills of lading and shipping labels. | Improved supply chain visibility and faster processing. |
As you can see, the core idea is the same everywhere: turn static, "dumb" documents into smart, actionable data. It's all about speed, accuracy, and freeing up your team to do more valuable work.
Choosing the Right OCR Solution for Your Needs
With so many OCR tools on the market, picking the right one can feel like a real chore. But here's the thing: not all solutions are created equal. What a massive corporation needs is likely way more than what a small business requires. The secret is to ignore the flashy marketing and zero in on what will actually help your unique workflow.
Making a smart decision really comes down to a few key factors: how accurate it is, how it plays with the software you already use, and if it can keep up as you grow. A little thought upfront will help you pick a tool that actually solves problems instead of just creating new ones.
Evaluating Accuracy and Document Types
First things first: how perfect does your data need to be? If you’re dealing with invoices, receipts, or legal contracts, you need an accuracy rate of 99% or higher. A tiny mistake there can lead to big, costly headaches. On the other hand, if you’re just digitizing old internal memos, a bit less accuracy is probably fine.
You also have to think about the kinds of documents you work with every day.
- Structured Documents: These are predictable, with a fixed layout. Think W-2s or standardized intake forms. Most basic OCR tools can handle these without breaking a sweat.
- Semi-Structured Documents: Invoices are the classic example here. The key info—like vendor, date, and total amount—is always there, but its location on the page can change from one invoice to the next. This is where you need a smarter, AI-driven tool.
- Unstructured Documents: These are free-form, like contracts or customer emails. Pulling specific data points from these usually requires a much more advanced system. To learn more, check out our guide on what is Intelligent Document Processing, which explains how AI tackles these trickier files.
Remember, a tool that's great at reading a clean, printed form might completely fall apart when faced with a slightly crooked scan of a vendor invoice. Always, always test a tool with your actual documents before you commit.
Considering Integration and Scalability
An OCR tool is only as good as its ability to slide right into your current workflow. If your team has to manually copy data from the OCR tool and paste it into your accounting software, you’ve just swapped one tedious task for another. Look for solutions that connect seamlessly, letting you export directly to a CSV that works with QuickBooks or Xero.
The goal of OCR is to eliminate friction, not relocate it. A solution that doesn’t integrate easily with your core software will quickly become a bottleneck in your workflow.
Scalability is just as important. Maybe you only handle a few dozen documents a week right now, but what happens in six months or a year? A good OCR platform should process a small batch of ten documents just as effortlessly as a batch of ten thousand.
Flexible, credit-based pricing models—like the one we offer at DocParseMagic—are perfect for this. They let you pay only for what you need, making it easy to scale up or down without being trapped in an expensive plan you don’t fully use. That way, the tool provides a clear return on investment as your business evolves.
Common Questions About OCR Technology
As you start to see the potential of Optical Character Recognition, some practical questions are bound to pop up. It's an incredible technology, but it’s not perfect. Knowing where it shines and where it stumbles is the key to getting the most out of it.
Let's dig into a few of the most common questions I hear from people new to OCR. The answers should give you a realistic idea of what to expect when you put it to work in your business.
How Accurate Is Modern OCR Technology?
This is usually the first thing people ask, and for good reason—accuracy is everything. The short answer is that modern, AI-powered OCR can be astonishingly precise, often hitting over 99% accuracy on clean, high-quality documents.
But that "high-quality" part is crucial. Several real-world factors can trip up the software and affect the final result:
- Image Quality: A blurry photo from a phone or a skewed scan will never perform as well as a crisp, high-resolution image. Think garbage in, garbage out.
- Font Complexity: Funky, decorative fonts are much harder for an algorithm to decipher than standard ones like Arial or Times New Roman.
- Document Layout: Complicated tables, multiple columns, or text layered over images can sometimes confuse the OCR engine about where to start reading.
This is exactly why the post-processing step we talked about earlier is so important. It acts as a safety net, using context and language models to spot and fix mistakes, which really bumps up the final accuracy. For most typical business documents like invoices and forms, a good OCR tool is more than reliable enough to automate your workflow.
Can OCR Read Handwritten Text?
Yes, absolutely—but this is where things get a bit more interesting. The technology for reading handwriting is technically called Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR), and it's built into most advanced OCR platforms.
However, the accuracy here can vary wildly. The system's success hinges entirely on how clear and consistent the writing is. Messy, loopy cursive is a world away from neat, printed block letters. While AI has gotten much better at interpreting different handwriting styles, it’s still a much tougher nut to crack than machine-printed text.
If your business relies on documents with a lot of handwriting—think signed approvals or notes scribbled in the margins of a form—you need to find an OCR tool that specifically advertises strong ICR capabilities. The only way to know for sure is to test it with your own real-world examples.
What Is the Difference Between OCR and Manual Data Entry?
This question cuts right to the chase of why OCR even exists. The difference is simple: automation versus human labor.
Manual data entry is exactly what it sounds like. A person sits down, reads a document, and physically types the information into a computer system. This process is always going to be:
- Slow: There’s a hard limit on how fast a person can type.
- Expensive: You're paying for every minute of that person's time.
- Prone to Errors: Even the most focused employee will make typos or misread a number eventually.
OCR, on the other hand, automates the whole thing. The software "reads" the document and pulls the information out digitally in seconds.
At its core, OCR is a technology built to eliminate the soul-crushing task of manual data entry. It frees up your team from mind-numbing repetition and lets them focus on work that actually requires a human brain, like analysis and decision-making.
Ready to stop typing and start automating? DocParseMagic uses powerful AI to extract data from your invoices, receipts, and forms directly into a spreadsheet in seconds. Try DocParseMagic for free and see how much time you can save.