
What Is OCR Technology Explained
Have you ever stared at a mountain of paperwork and wished you could just wave a magic wand to get all that information into your computer? That's essentially what Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology does. It’s a smart process that converts images of text—whether from a scanned document, a photograph of a receipt, or a PDF—into actual, editable text data that a computer can understand and work with.
Think of it as a digital translator for the written word. It sees a picture of a document and, instead of just seeing pixels, it reads the letters and numbers, turning a static image into live, searchable text you can copy and paste.
Understanding OCR Technology in Simple Terms

Imagine you have a 100-page printed report and need to get all of it into a spreadsheet. The thought of manually typing every single word is enough to make anyone's fingers ache. It's a tedious job, an open invitation for typos, and a massive time sink.
Now, what if you had a tool that could "read" that entire report in seconds and type it out for you perfectly? That's the real power of OCR. It's the bridge connecting our physical, paper-based world with the digital one.
This technology is already all around us. It’s the magic that lets you deposit a check by taking a photo with your phone, and it’s why you can search for a specific phrase inside a PDF that you know was originally a paper scan.
The Core Function of OCR
At its very heart, OCR is all about automating data entry. It takes a human out of the loop of reading something and then typing that same information into a computer system. This simple function has huge ripple effects on business efficiency, practically eliminating one of the most repetitive and error-prone tasks in any office.
By transforming static images into dynamic, usable data, OCR unlocks information that was previously trapped in paper files or image-only PDFs. This makes data searchable, editable, and ready for analysis.
For an accounting team, this is a game-changer. They can use OCR to automatically pull key details—like invoice numbers, dates, and totals—from hundreds of supplier invoices without ever touching a keyboard.
This leads to some immediate, tangible benefits:
- Increased Speed: A stack of documents that might have taken all afternoon to process manually can be finished in just a few minutes.
- Reduced Errors: Automation sidesteps the inevitable typos and data entry mistakes that happen when we're tired or distracted.
- Improved Accessibility: Once digitized, information becomes instantly searchable. Finding a specific invoice from two years ago is as easy as a keyword search.
To give you a clearer picture, here’s a quick breakdown of OCR’s main jobs.
Core Functions of OCR Technology at a Glance
| Function | Description | Example Application |
|---|---|---|
| Image-to-Text Conversion | Transforms pixels in an image representing characters into machine-readable text code (like ASCII or Unicode). | Scanning a printed book page and turning it into an editable Word document. |
| Data Extraction | Identifies and isolates specific pieces of information from a document, such as names, dates, or totals. | Pulling the "Total Amount Due" and "Vendor Name" from a photographed invoice. |
| Document Indexing | Makes the full text of a document searchable, allowing for easy retrieval based on its content. | Uploading a scanned contract and later finding it by searching for a specific clause. |
This table shows just how foundational OCR is to modern data management.
Ultimately, getting a handle on OCR is the first step to seeing how powerful automation tools, like DocParseMagic, can completely reshape business operations. It’s not just about turning pictures into words; it’s about making your information work for you.
The Journey of OCR From Concept to Commerce
To really get a feel for what today's OCR can do, it’s helpful to rewind and see where it all started. The idea of a machine that could read isn't some new-age concept—it’s a dream that took decades to become a practical reality. The journey was long, filled with breakthroughs that built the foundation for the tools we rely on now.
The first hurdle was a big one: how do you teach a machine to recognize something as varied and nuanced as the alphabet? Early successes were incredibly limited, only able to read a single, specific font. Imagine someone who can only understand one person's handwriting—it's a start, but hardly versatile.
From Single Fonts to Broader Horizons
A huge leap forward came with the creation of standardized, machine-readable fonts like OCR-A. This font, with its clean and simple characters, was designed specifically for computers to read without confusion. This was a critical step that opened the door to the first real-world uses of OCR, even if it meant people had to type things in a way the machine could understand.
These early applications were revolutionary for their time. The technology got its official name in 1959 when IBM launched a system for data capture. Throughout the 1960s, institutions like MIT dove deep into research, and big names started putting OCR to work. Reader's Digest used it to process coupon serial numbers, and the U.S. Postal Service began testing it to sort mail—an experiment that would eventually change postal services worldwide. You can dig deeper into this early history and its connection to modern automation at RPA Tech.
The real game-changer was the move from single-font systems to omni-font OCR. This was the moment the technology started learning to read more like a human, recognizing text in all sorts of styles, sizes, and formats.
This evolution from rigid, one-font readers to flexible omni-font systems was the turning point. Suddenly, OCR became commercially viable on a massive scale. Instead of forcing our documents to fit the machine, the machine started adapting to our documents.
Setting the Stage for Modern AI
This backstory matters because it shows just how much innovation it took to get from a clunky machine reading one font to the sophisticated systems we have today. Every step, from the first commercial reader to omni-font recognition, was a crucial piece of the puzzle.
Here are a few key milestones:
- 1950s: The first commercial OCR systems appear, designed to read specific, stylized text.
- 1960s: Major players like the U.S. Postal Service start using OCR for massive sorting jobs.
- 1970s: The invention of omni-font OCR gives machines the ability to read multiple fonts, blowing the doors open for new uses.
Understanding this history helps put modern tools like DocParseMagic into perspective. They are built on the shoulders of decades of research, using artificial intelligence not just to see text, but to understand its meaning and context in ways the early pioneers could only dream of.
How OCR Technology Turns Images into Text
To really get what OCR is all about, you have to look under the hood. The whole process is less of a single magic trick and more like a careful, multi-step assembly line. Think of it like teaching someone to read for the first time—it’s a sequence of logical steps, each one building on the last to make sure the final result is spot-on.
It all boils down to three core stages. First, the software gets the document ready to be read. Next, it actually figures out what each letter and number is. Finally, it gives everything a final proofread to catch any silly mistakes.
Stage 1: Image Pre-processing
Before the software can even attempt to "read" anything, it has to clean up the image. This is all about making the text as clear and easy to see as possible. It's the digital equivalent of wiping smudges off your glasses, straightening a crooked page, and turning on a brighter light before you start reading a book.
This image pre-processing step is absolutely critical. The quality of the image you start with has a huge impact on how accurate the final text will be.
Here are a few of the common cleanup jobs the software tackles:
- Deskewing: If you've ever scanned a page and it came out slightly crooked, this is the fix. The software digitally straightens the lines of text so they're perfectly horizontal.
- Noise Removal: This gets rid of all the random specks, stray dots, or dark shadows on the page that aren't actually part of the text.
- Binarization: The image is converted into simple black and white. This creates a really sharp contrast between the characters and the background, leaving no room for ambiguity.
Without this prep work, the system would be lost, just like you would be trying to read in a shaky, dimly lit room. It’s why a crisp, clean scan always yields better results.
This infographic gives a great visual of how far OCR has come over the years.
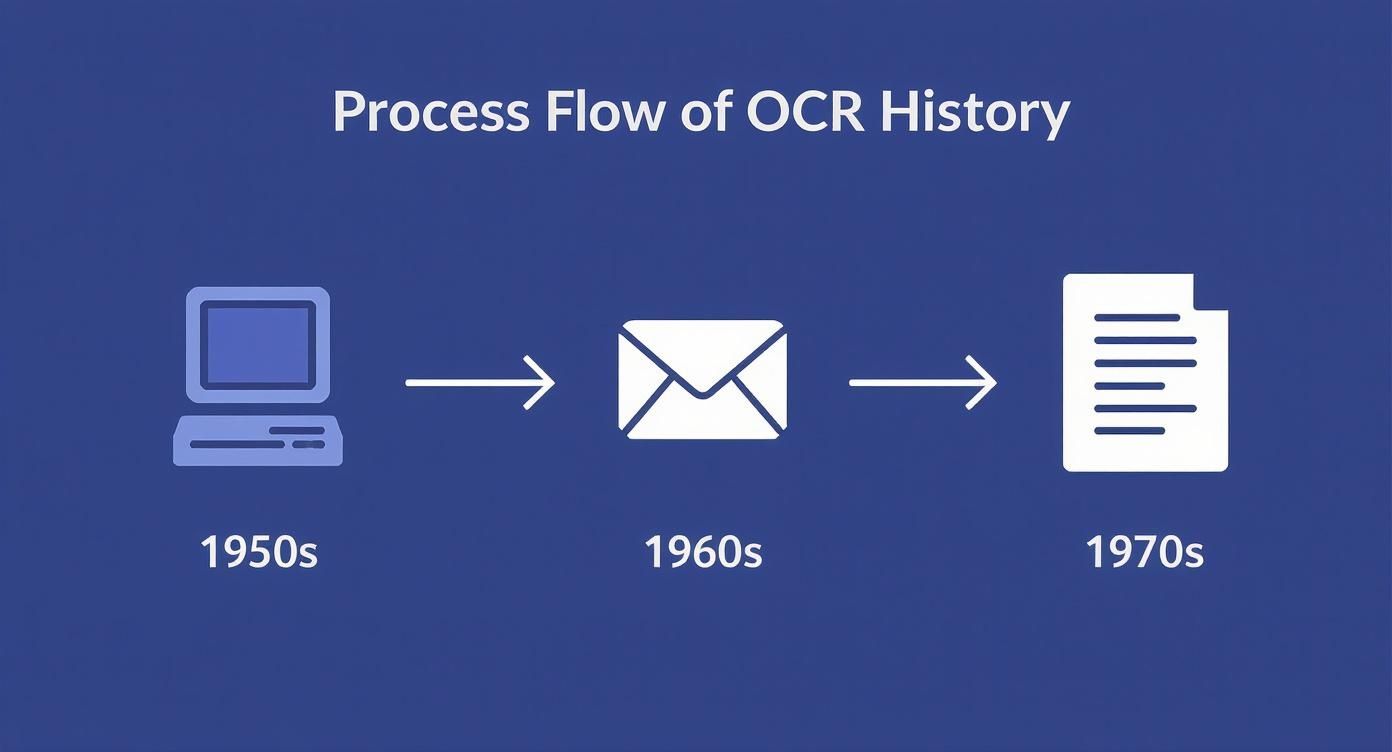
As you can see, we've moved from clunky, limited systems to the incredibly versatile tools we have today, which brings us to the next step.
Stage 2: Character Recognition
With a clean, prepped image ready to go, the real work begins. This is the character recognition phase—the part where the software actually analyzes the shapes on the page and identifies every single letter and number.
There are two main ways it does this:
- Pattern Matching: This is the old-school method. The system has a library of fonts and characters stored in its memory. It takes a shape from the document and tries to find a perfect match in its library, a bit like a toddler's shape-sorting toy. If it finds a match for an "A," it knows it's an "A."
- Feature Detection: This is the much smarter, AI-powered approach. Instead of looking for a perfect match, the software breaks each character down into its fundamental components—the lines, curves, and loops that form it. It recognizes an "A" by identifying its two angled lines and the horizontal bar connecting them. This technique is far more flexible, allowing it to read thousands of different fonts and even some styles of handwriting.
It’s this AI-driven feature detection that makes modern OCR tools so powerful. They've moved way beyond the rigid limitations of earlier systems.
Stage 3: Post-processing
The last step, post-processing, is basically the software’s built-in spell-checker and editor. After the image has been converted into raw text, the system scans through it one last time to make sure everything makes sense in context.
This is where the machine stops just seeing shapes and starts understanding language. It uses massive dictionaries and language models to spot and fix things that don't look right.
For example, if the OCR accidentally read "invoice" as "invo1ce," the post-processing engine would flag it. It knows "invo1ce" isn't a real word and, based on the surrounding text, would intelligently correct it to "invoice." This final quality check is what makes the data reliable enough for business. If you’re processing a high volume of documents, this step is non-negotiable for getting automation right. You can see how this works in practice in our guide to PDF data extraction to Excel.
From Basic OCR to Intelligent Document Processing
The difference between the OCR of yesterday and the intelligent tools we have today is night and day. Early OCR was a fantastic idea, but it was rigid. It often stumbled on anything that wasn't a very specific, pre-programmed font. In a world full of different typefaces, messy layouts, and inconsistent document quality, that was a huge problem.
The first real breakthrough came in the 1970s. That’s when Ray Kurzweil developed what he called omni-font OCR—a system that could finally recognize text in almost any style. His company, Kurzweil Computer Products, introduced it in 1974, and it completely changed the game. Suddenly, OCR wasn't just a niche tool; it could be used to digitize books, newspapers, and all sorts of real-world documents. You can read more about this turning point in the history of OCR on Incode.com.
This leap forward set the stage for the next major evolution: the arrival of artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Beyond Just Reading to Actually Understanding
Modern OCR doesn't just play a simple matching game, comparing shapes to a library of letters. It uses AI, especially neural networks, to figure out a document's layout, structure, and context. This is the critical difference between old-school text recognition and what we now call Intelligent Document Processing (IDP).
Think of it this way: traditional OCR answers the question, "What does this text say?" IDP, on the other hand, answers, "What does this text mean?" An older system might correctly read the characters "$500.00," but an intelligent one knows that this is the "Total Amount Due" on an invoice because it sees the label next to it and its position on the page.
AI-driven systems have pushed accuracy to over 98%, but the real magic is in their ability to understand context. They can handle messy handwriting, low-quality scans, and complicated tables that would completely baffle simpler software.
It’s this ability to interpret, not just read, that makes today’s tools so powerful for business.
The Power of AI-Driven Context
This shift to AI fundamentally changes how you process documents. Instead of just getting a jumbled wall of text, you can now automatically pull out structured, meaningful data.
This smarter approach gives you a few key advantages:
- Contextual Extraction: The AI can pinpoint and grab specific data points—like a vendor's name, individual line items, or tax amounts—no matter where they are on the page.
- Data Validation: The system can cross-reference information on the fly. For instance, it can check if the line items actually add up to the total amount, flagging potential errors instantly.
- Continuous Learning: Thanks to machine learning, the models get better with every document they process. They learn your document formats and become more accurate over time.
This evolution is what makes modern OCR so much more than a simple digitization tool. To see just how far it's come, check out our complete guide on what is intelligent document processing and how it drives automation. This is the intelligence that powers tools like DocParseMagic, turning a tedious, manual chore into a fast, accurate, and hands-off process.
Where OCR Technology Shines in the Real World
It’s one thing to understand how OCR works on a technical level, but it’s another to see it solving real-world problems. This isn’t just abstract theory; it's a practical tool that has become a quiet engine of efficiency in countless industries.
You've probably used it today without even realizing it. Ever deposited a check by snapping a picture with your banking app? That's OCR at work, reading the numbers and amounts for you. It's become so woven into our daily tools that we often don't notice it's there.
A Game-Changer for Accounting and Finance
If there's one department that has been completely transformed by OCR, it's accounting. Finance teams have always been swamped by a never-ending flood of invoices, receipts, and expense reports—all demanding hours of careful, manual data entry.
Modern OCR flips that script entirely. An employee no longer has to spend their afternoon tediously keying invoice details into a spreadsheet; an OCR system can pull that same data in a matter of seconds. This is especially powerful for high-volume, repetitive work. If you want to see just how deep this goes, you can learn more about how to automate invoice processing and the specific benefits it brings.
By automatically grabbing key information like vendor names, due dates, and line-item totals, OCR slashes human error and frees up skilled accounting professionals to focus on financial strategy instead of just typing.
And it's not just about invoices. Banks use this technology to process loan applications and digitize customer forms. Insurance companies rely on it to accelerate claims by lifting information from accident reports and medical bills. The common denominator is simple: it breaks the manual data bottleneck.
Beyond the Balance Sheet: Logistics and Healthcare
The impact of OCR stretches far beyond the world of finance. Take the logistics and shipping industry, where speed and accuracy are everything.
- Tracking Packages: OCR scanners read shipping labels in a flash, updating tracking information as packages fly through sorting centers.
- Managing Inventory: Warehouse workers use OCR to scan part numbers on boxes, keeping stock counts accurate and up-to-date.
In healthcare, fast access to accurate records can be a matter of life and death. OCR helps digitize patient histories, lab results, and insurance paperwork, making a patient's entire file instantly searchable for doctors and nurses. This drastically improves the speed and quality of care.
Legal teams also lean on OCR to convert mountains of old case files and contracts into searchable digital databases. What used to be days of digging through dusty boxes can now be done in minutes with a simple keyword search. From tracking a simple package to helping a doctor make a critical decision, OCR has become an indispensable part of getting things done.
Key Business Benefits of Adopting OCR
Knowing what OCR technology is and how it works is one thing. But the real question is, what can it actually do for your business? Shifting from manual, paper-heavy workflows to an automated, digital system creates a ripple effect of improvements that touch nearly every part of your operations.
One of the most immediate impacts you'll see is on your bottom line. Manual data entry is a resource black hole—it eats up employee hours that could be spent on tasks that actually grow the business. By automating this grunt work with OCR, you reclaim that time and significantly cut down on labor costs.
Boosting Accuracy and Efficiency
Let's face it, humans make mistakes. Even your most detail-oriented employee can mistype a number after staring at a stack of invoices for a few hours. OCR systems don't have that problem. They don't get tired, bored, or distracted, which means your data becomes far more accurate.
This isn't just about clean data for its own sake. Higher accuracy prevents a whole host of expensive problems, like overpaying a vendor or basing a financial forecast on bad numbers. You end up with a solid, trustworthy data foundation to build on.
By automating document processing, businesses can shrink workflows that once took days down to just a few minutes. An accounting team can power through a hundred invoices in the time it used to take to manually process a handful.
This speed creates some powerful advantages:
- Faster Payments: When invoices get processed instantly, you can settle up with vendors faster and often take advantage of early payment discounts.
- Smarter Decisions: With up-to-the-minute data, leaders can make strategic calls with confidence, not guesswork.
- Effortless Scalability: As your business grows, your team can handle a much larger volume of documents without needing to hire more people just for data entry.
Unlocking Your Data Archives
Think about all the information sitting in your company's filing cabinets or trapped in static PDF scans. For many businesses, this amounts to decades of valuable data that's completely inaccessible. OCR is the key that unlocks it, turning those dormant archives into a searchable, dynamic resource.
Imagine you need to pull up every contract you've signed with a specific client over the last 10 years. The manual way would be a nightmare of digging through dusty boxes. Once those documents are digitized with OCR, it’s a simple keyword search that takes seconds. This makes audits and compliance checks a breeze and turns your old paperwork into a goldmine for business intelligence.
To really see the difference, let's compare a few common business tasks with and without OCR.
OCR Technology Impact on Business Operations
Here’s a side-by-side look at how much changes when you automate document processing.
| Business Process | Manual Approach (Without OCR) | Automated Approach (With OCR) |
|---|---|---|
| Invoice Processing | An employee manually reads each invoice, types data into the accounting system, and routes it for approval. The process is slow and prone to errors. | OCR automatically extracts data (vendor, amount, date), validates it against existing records, and initiates the approval workflow in seconds. |
| Expense Reporting | Employees collect paper receipts, fill out a spreadsheet, and submit it. Finance then manually reviews and enters each line item. | Employees snap a photo of a receipt. OCR extracts the key details and auto-populates the expense report, which is then submitted digitally. |
| Client Onboarding | A new client fills out paper forms. An admin manually transcribes the information into the CRM, which can lead to delays and typos in contact details. | The client fills out a digital or scanned form. OCR instantly pulls the information and creates a new, accurate client profile in the CRM. |
| Data Archival & Retrieval | Documents are stored in physical filing cabinets or as non-searchable image files. Finding a specific document can take hours or even days. | All documents are digitized, and their text is made searchable. Anyone can find a specific file in seconds using a simple keyword search. |
The contrast is pretty stark. Moving to an OCR-based system isn't just a minor upgrade; it fundamentally changes how work gets done, freeing up your team to focus on what really matters.
Common Questions About OCR
As you get familiar with OCR, a few questions tend to pop up again and again. Let's tackle them head-on to give you a clearer picture of what the technology can—and can't—do.
How Accurate Is It, Really?
Modern OCR is remarkably accurate. Thanks to a huge boost from AI and machine learning, today’s top-tier systems can often hit 98% accuracy or even higher on clean, clear documents. This isn't just a lab number; it's the kind of reliability that businesses build entire workflows around. You can dig into the full history of these improvements on the Wikipedia page for OCR.
That said, it’s not magic. Accuracy can still take a hit from things like poor image quality, crumpled paper, or really unusual document layouts. For those can't-get-it-wrong situations, many teams will add a quick human check at the end to close that tiny gap and ensure everything is perfect.
Can It Actually Read Handwriting?
Yes, but this is where things get tricky. The technology for reading handwriting is typically called Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR), and it's a much bigger challenge than reading printed text.
The results depend entirely on the handwriting itself. Neat, consistent block printing? No problem. A doctor's frantic scribble on a prescription pad? That's a different story. The good news is that ICR models are constantly learning from new examples, so they're getting smarter all the time.
OCR turns a picture of text into a block of raw text. Data capture, on the other hand, is the art of finding and pulling out specific pieces of information—like an invoice number or a total amount—from that raw text and putting it into a structured format.
It's a crucial difference. OCR gives you the ingredients, but data capture is the recipe that makes them useful.
Ready to stop manual data entry for good? With DocParseMagic, you can turn invoices, receipts, and forms into structured spreadsheet data in under a minute. Get started for free at docparsemagic.com.