Automate Data Entry A Practical Guide to Smarter Workflows
If your team is drowning in manual data entry, you already feel the pain. It’s not just the hours lost to copy-pasting; it’s the domino effect of typos, project delays, and the sheer monotony that drains your best people. The reality is, bad data from manual entry mistakes costs businesses a fortune. The whole point here is to get your team off the hamster wheel of repetitive tasks and onto strategic work that actually moves the needle.
But before you can jump to a solution, you have to get a clear diagnosis of the problem. That means taking a hard look at your current data entry processes. This isn't about pointing fingers—it's about finding the weak spots in the system itself.
Think of it like a mechanic listening to an engine. You need to find out exactly where the noise is coming from before you can fix it.
Finding Your Biggest Automation Opportunities
First things first, get your team together and literally map out every single place where someone is typing data by hand. Don't skip the "small stuff." The goal is a complete picture of your data flow, so you can see exactly where the logjams are.
For each manual task you identify, ask these questions:
- How much and how often? Are we talking about 10 invoices a week or 100 a day? A task that happens constantly is a prime candidate for automation.
- How much time does it really take? Be honest here. If three people spend two hours a day processing orders, that's 30 hours a week of skilled labor you could be using for something else.
- Where are the mistakes creeping in? Are customer addresses getting botched? Are invoice amounts off? Do purchase order numbers not match? High error rates are a massive red flag screaming for automation.
- Is the data messy or clean? Is it coming from a nice, neat form (structured data) or from all over the place like emails and PDFs (unstructured data)? Simple, structured data is usually the easiest place to start and get a quick win.
When you put real numbers to the time and cost of each task, the need for change becomes undeniable. The conversation shifts from, "This is a hassle," to, "This is costing us $50,000 a year in lost productivity."
Building Your Action Plan
Once you've done the audit, you can build a simple, prioritized list. Rank each task by looking at the potential time savings, the impact of getting rid of errors, and how easy it would be to automate. For most businesses, processing invoices usually shoots to the top of the list because it's high-volume and directly tied to cash flow.
This gives you a clear roadmap. Instead of trying to boil the ocean, you can tackle the problems that will give you the biggest return, fast.
The technology that makes this happen falls under the umbrella of intelligent document processing, which is designed for exactly these kinds of messy, real-world challenges. Taking this first step seriously ensures you choose a tool that solves your most expensive problems first.
Choosing Your Automation Approach
Once you’ve pinpointed the data entry tasks gumming up the works, it’s time to pick the right tool for the job. The business automation market is booming—it's set to jump from $13 billion to $23.9 billion by 2029—which can make choosing a solution feel overwhelming.
With 66% of businesses already automating at least one process, and that figure expected to climb to 85%, sitting on the sidelines isn’t really an option anymore.
The most important factor in your decision is the type of documents you’re working with. Are they all the same, or does every new document look completely different? Matching the tool to your specific documents is the secret to a successful automation project.
This decision guide can give you a solid starting point for figuring out what—and when—to automate.
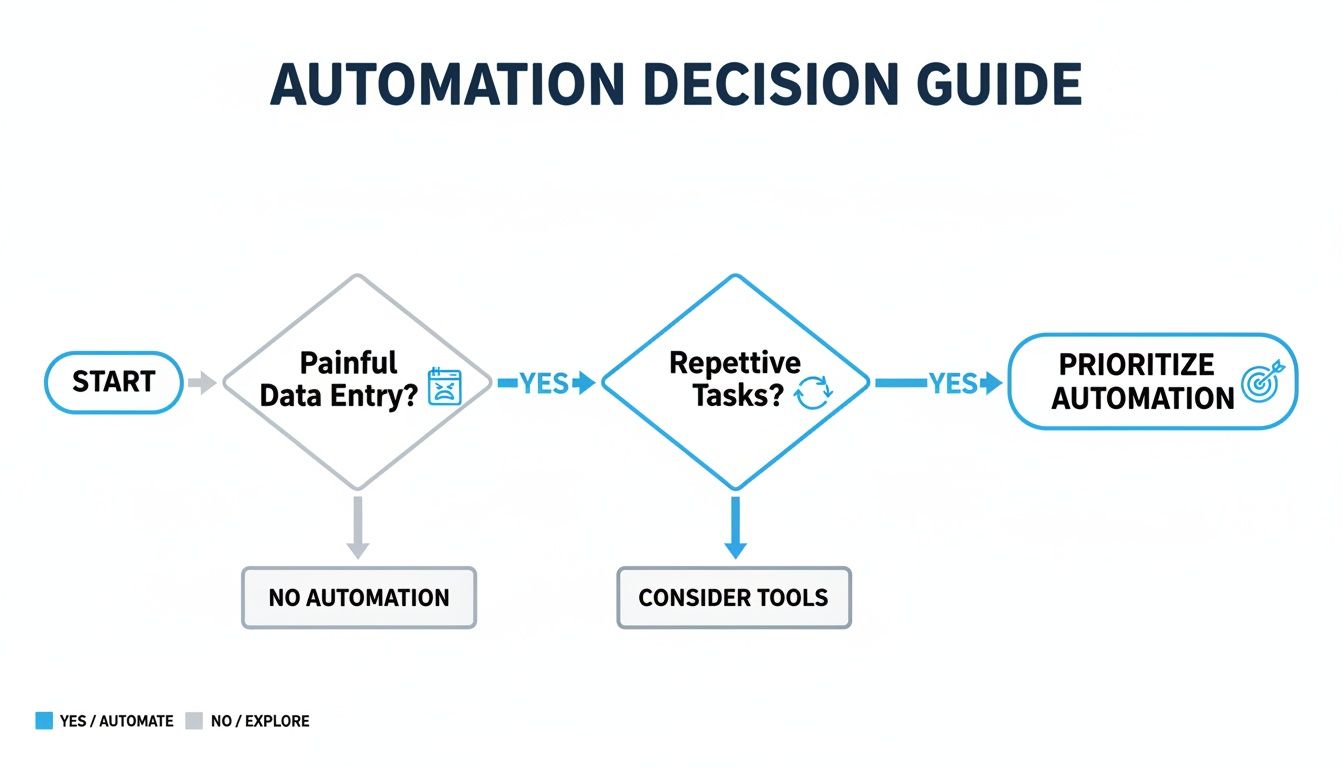
As the flowchart shows, the journey starts by identifying those painful, repetitive tasks and then finding a solution that’s built to handle them.
Comparing Data Entry Automation Methods
There are a few primary ways to tackle data entry automation. Each has its strengths, so understanding the landscape will help you choose wisely. The main options include template-based tools, AI-powered platforms, and Robotic Process Automation (RPA).
Let's break down how they compare.
| Method | Best For | Complexity | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Template-Based Tools | Highly structured documents with fixed layouts (e.g., internal forms, invoices from a few key vendors). | Low | $ - $$ |
| AI-Powered Platforms | Unstructured or semi-structured documents with varied layouts (e.g., invoices from many different suppliers). | Medium | $$ - $$$ |
| Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Workflows requiring data transfer between multiple, disconnected software applications. | High | $$$ - $$$$ |
Ultimately, the best method is the one that solves your specific problem without adding unnecessary complexity or cost. A simple, predictable workflow doesn't require a high-end AI solution, but trying to use a basic template tool for a chaotic process will only lead to headaches.
Template-Based vs. AI-Powered Tools
One of the first big decisions is whether you need a template-based parser or a more advanced AI-driven platform. Getting this right is critical.
-
Template-Based Tools are perfect when your documents are consistent and predictable. Imagine you get hundreds of invoices a month, but they all come from just three suppliers who never change their invoice format. You'd set up a template for each one, telling the software exactly where the "Invoice Number" or "Total" is located every single time. It's rigid, but incredibly reliable for standardized documents.
-
AI-Powered Tools are what you need for variety and unpredictability. If you process invoices from hundreds of different vendors, each with its own unique layout, a template-based system would be a maintenance nightmare. AI models don't need fixed locations; they read and understand the document's context to find the right data, no matter where it appears.
A small firm using its own standardized expense forms could easily get by with a template-based tool. On the other hand, a purchasing department sifting through proposals from vendors worldwide absolutely needs an AI solution to handle all the different formats. If you want to go deeper on this, take a look at our guide on document data extraction software.
Key Takeaway: Don't pay for power you don't need. If your documents are uniform, a template-based system is a solid, cost-effective choice. But if you're dealing with a mixed bag of formats, investing in AI is the only way to scale effectively.
When to Consider Robotic Process Automation
Sometimes, pulling data from a document is only half the battle. The real pain comes from moving that data between different, disconnected systems. That’s where Robotic Process Automation (RPA) comes in.
Think of RPA "bots" as digital employees that mimic human actions. They can log into apps, copy-paste information, fill out forms, and move files around—just like a person, but way faster and without making typos.
For example, a logistics company might get shipping orders as PDF attachments. A person’s workflow would be:
- Open the PDF.
- Manually type the customer's name, address, and order into the company's ERP.
- Log into a separate shipping carrier's website to schedule the pickup.
- Finally, copy the tracking number back into a shared spreadsheet.
An RPA bot can do all of that automatically. It would extract the data from the PDF and then perform all the clicks and keystrokes needed to update every system. If your process involves a lot of manual "swivel-chair" work between applications that don't talk to each other, RPA is probably the solution you're looking for.
Building Your First Automation Workflow
Theory is one thing, but rolling up your sleeves and actually building something is where the magic happens. Let's get practical and walk through setting up your first real automation workflow. The good news? You don't need to be a developer. Modern tools are built for the people who actually do the work.
We'll use a scenario that’s probably all too familiar: processing purchase orders. Our goal is simple—teach the software how to find and pull out key info like the PO number, date, and total amount. Once you set this up, you won't have to type that information ever again.
Defining Your Data Fields
First things first, you have to tell the system what you want it to find. Forget about lines of code. With today's document parsing tools, it’s all visual. You just upload a sample purchase order and start pointing and clicking.
Think of it like this: you’re looking at a PDF of a PO. To grab the invoice number, you’d literally draw a box around "INV-12345" and tell the tool, "This is the Invoice Number." You do the same thing for every other piece of data you need.
For a standard purchase order, you'd likely define fields like these:
- PO Number: The unique code for that order.
- Vendor Name: Who sent you the document.
- Order Date: When the transaction happened.
- Line Items: The list of products or services, with quantities and prices.
- Total Amount: The final bill.
What you're really doing is creating a template. You're giving the software a map, showing it what an "Invoice Number" looks like and where it usually lives on that specific layout.
Creating Robust Extraction Rules
Of course, the world isn't perfect. Your vendors won’t always use the exact same format. One month, an invoice date might be "10/31/2024," and the next, it’s "October 31, 2024." A good workflow needs to handle these little inconsistencies, and that's where smart rules come in.
Instead of telling the tool to only look in one specific spot, you can give it more flexible instructions. For instance, you could create a rule that says, "Find the text that comes right after the words 'Invoice No.' or 'Invoice #.'" This makes your setup much more resilient when someone makes a small change to their document layout.
This is what separates basic automation from intelligent automation. A rigid system will break the moment a vendor updates their invoice template. An intelligent one adapts because it understands the context of the data, not just its coordinates on a page.
You also have to account for hiccups with Optical Character Recognition (OCR). That's the tech that turns a scanned image into real text. It's incredibly powerful, but it's not foolproof—it might mistake a "5" for an "S" or a "0" for an "O." The best automation tools let you set up validation rules to catch these gremlins, like flagging a "Total Amount" field if it contains letters, so you can give it a quick manual check.
Handling Line Items and Tables
Grabbing a single data point like a total is great, but the real soul-crushing work is often in the tables—the line items on an invoice, commission details on a sales report, you name it.
Automating this is surprisingly simple. Most tools let you define the table structure visually.
- First, you highlight the entire table area on your sample document.
- Then, you name your columns: "Product ID," "Description," "Quantity," "Unit Price," etc.
- The software's AI takes it from there, figuring out where each row begins and ends and capturing all the data for you.
This is a genuine game-changer. An invoice with 20 line items that would take a solid ten minutes to enter by hand can be processed in just a few seconds. Honestly, this feature alone is often what makes a team decide to go all-in on automation. To see how this fits into the bigger operational picture, check out our guide to document workflow automation.
Once you've defined your fields, built some smart rules, and taught the system how to read tables, you have a reliable, repeatable workflow. You've successfully trained a machine to read your documents, freeing up your team for more important things. The next step is to get this clean, extracted data into your other business tools.
Let's Connect Your Data: Integrating With Your Business Systems
Getting clean data out of your documents is a fantastic first step, but it's not the final one. The real magic happens when that information flows directly into the software you rely on every day, like your accounting platform or CRM. This is where automation moves from being a neat trick to becoming the backbone of your operations.
The goal is to build a seamless pipeline from document to system. Imagine an invoice lands in your inbox, your tool grabs the key details, and a draft bill instantly appears in QuickBooks for your review. No more copy-pasting. No tedious manual entry. Just a smooth, hands-off workflow.
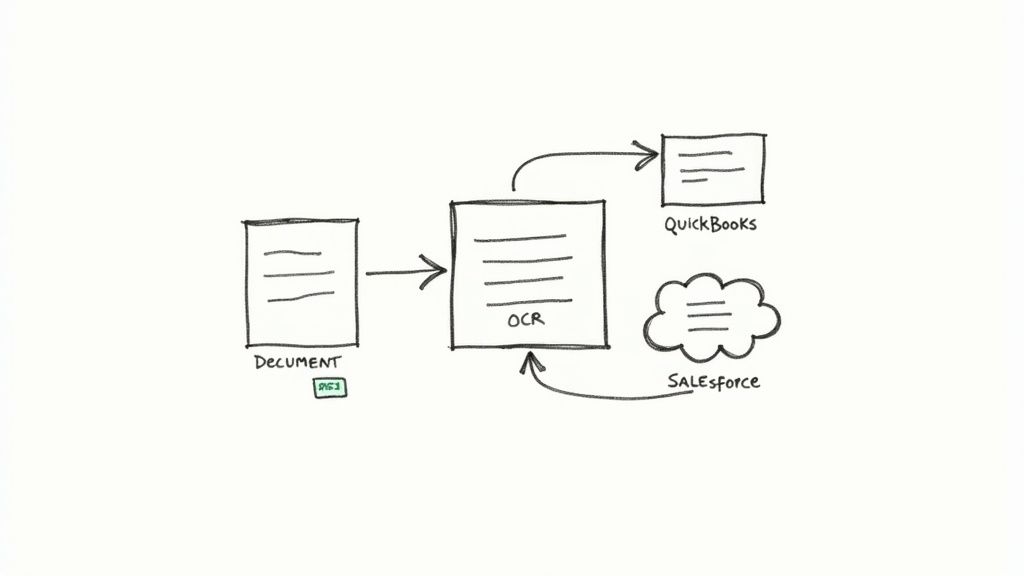
This kind of end-to-end connection is what it truly means to automate data entry, turning a simple extraction task into a fully automated business process.
Mapping Data to Its Final Destination
The first thing you'll do is called data mapping. It sounds technical, but it’s really just about telling your software where to put the information it just extracted. You're basically creating a set of instructions connecting the data points from your document to the right fields in your business software.
It’s as simple as this:
- The "Vendor Name" from an invoice gets sent to the "Supplier" field in QuickBooks.
- The "Total Amount" goes into the "Bill Total" field in Xero.
- A new lead's "Email Address" from a contact form lands in the "Email" field in Salesforce.
Most modern tools, including our example DocParseMagic, have a visual, drag-and-drop interface for this. You’re literally drawing lines from point A to point B, creating a reusable template for every similar document that comes through.
For businesses that handle massive amounts of information, integrating this newly structured data into a central data warehouse is often the next step. If you're managing data at that scale, it can be helpful to Learn more about collaborating with data platform partners like Snowflake.
Choosing Your Integration Method
There are a few ways to get your systems talking, and the best one for you depends on your needs and how technical you want to get.
- Direct API Integrations: This is the most solid and reliable method. Many data extraction tools offer built-in connections to popular platforms like QuickBooks, Xero, or Salesforce. You set it up once, and the data flows automatically from then on.
- Middleware Platforms (like Zapier): Think of these as universal adapters. Tools like Zapier or Make let you connect thousands of different apps without writing a single line of code. You can create simple but powerful recipes, like: "When a new invoice is parsed in DocParseMagic, create a new row in my Google Sheet."
- Clean CSV/Excel Exports: Don't overlook the simple solutions. Sometimes, all you need is a perfectly formatted spreadsheet to upload. This is a fantastic, no-fuss approach for batch uploads, monthly reports, or working with systems that don't offer modern integrations.
My Advice? Start with the simplest method that gets the job done. A clean CSV export that saves you two hours a week is a much bigger win than a complicated API project that you never quite get around to finishing.
Building a Safety Net with Validation Rules
Letting a machine handle everything can feel a little unnerving at first. What if it gets something wrong? This is where you build in a safety net with validation and business rules. They give you the speed of automation with the critical oversight of a human, creating what’s known as a "human-in-the-loop" workflow.
You can set up simple rules to flag anything that looks out of the ordinary for a quick manual check.
- Flag high-value invoices: Automatically pause any invoice over $5,000 and send it for manual approval before it gets paid.
- Check for missing data: If a document is missing a required field, like a PO number, send it to a review queue instead of pushing it through.
- Validate totals: Have the system check if the sum of the line items matches the invoice total. If not, flag it as a potential error.
These rules give you the confidence to let the system run. You get massive efficiency gains on 95% of your documents while ensuring an expert eye always checks the exceptions.
The impact here is enormous. Studies show automation can cut down manual data entry work by up to 80%. Even better, automated systems can achieve accuracy rates between 99.959% and 99.99%. That’s a tiny one to four errors per 10,000 entries, compared to the 100 to 400 errors a human might make in the same batch. This frees up your team from mind-numbing tasks so they can focus on work that actually matters.
Measuring Success and Proving Your ROI
So you’ve set up your new automated data entry system. It feels faster, looks slicker, and your team is definitely happier. But "feeling" faster doesn't get you budget approval for the next project. To truly prove the value of your work, you need to speak the language of business—and that means numbers.
Justifying the investment in automation, whether it's software costs or the time you spent setting it up, requires a clear-eyed look at the return on investment (ROI). It's about moving beyond anecdotal wins and building a rock-solid business case with cold, hard data.
Key Metrics For Automation ROI
To build that case, you need to track the right things. I’ve found that focusing on a few core metrics gives you a powerful before-and-after picture that makes the benefits crystal clear.
Here's a breakdown of the essential metrics to track for evaluating the success of your data entry automation initiatives.
| Metric | How to Measure | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Time Per Document | Time an employee from start to finish on one manual document (like an invoice). Compare that with the automated time. Simple. | This is your most direct efficiency gain. Shaving the time from 5 minutes down to 30 seconds per invoice is a massive win when you multiply it by hundreds or thousands of documents. |
| Error Rate Reduction | Grab a sample batch of manually entered data and count the errors—typos, wrong numbers, you name it. Then, compare that to the error rate from your new automated workflow. | Fewer errors mean less time wasted on detective work and fixes. It also means more trustworthy data for reports and financial planning, which is a huge deal. |
| Employee Hours Reclaimed | Calculate the total hours your team spent on manual entry each week or month before you flipped the switch on automation. | This is the metric that really resonates with leadership. It reframes the conversation from cutting costs to creating capacity for higher-value work, like analysis or customer follow-up. |
When you track these data points, you're no longer just saying the process is "better." You're proving it’s 90% faster and 99% more accurate. Those are the kinds of numbers that get attention.
Calculating Your Financial Return
Once you have these operational metrics, translating them into dollars and cents is surprisingly straightforward. This is where you connect the dots for the finance team.
Let's walk through a real-world example I see all the time.
A small business processes about 500 vendor invoices every month. Their accounts payable clerk, who earns $25 an hour, spends an average of 6 minutes on each one—opening the email, finding the key data, and punching it into QuickBooks.
- The Old Way (Manual Costs):
- Total Time: 500 invoices × 6 minutes/invoice = 3,000 minutes a month.
- Total Hours: That's 50 hours every single month.
- Labor Cost: 50 hours × $25/hour = $1,250 per month.
- Annual Labor Cost: A whopping $15,000 just for this one task.
Now, they sign up for a tool like DocParseMagic for $150 a month ($1,800 a year). The system now processes each invoice in about 30 seconds. They decide to have the clerk spend one minute reviewing the trickier 10% of invoices for exceptions.
The real power of automation isn't just in the speed of the machine; it's in freeing up your most valuable resource—your people—to think, strategize, and solve problems.
The Bottom-Line Impact
With the new workflow in place, the time commitment practically vanishes, and the financial savings become undeniable. If you want to dive deeper into this topic, especially around sales data, check out this CRM Automation Vs Manual Data Entry ROI Comparison.
- The New Way (Automated Costs):
- New Time: (500 invoices × 0.5 minutes) + (50 exceptions × 1 minute) = 300 minutes.
- New Hours: That’s just 5 hours per month.
- New Labor Cost: 5 hours × $25/hour = $125.
- Total Monthly Cost: $125 (labor) + $150 (software) = $275.
- Annual Cost with Automation: $275 × 12 = $3,300.
By making this one change, the company saves $11,700 a year ($15,000 - $3,300). Even better, they've reclaimed 45 hours of their skilled clerk's time every single month—time that can now be spent on financial analysis, vendor relations, or chasing down late payments.
That’s how you prove your ROI.
Solving Common Automation Challenges
Starting an automation project is exciting, but let's be real—it's never a "set it and forget it" deal right out of the gate. Real-world documents are messy. They show up with inconsistent layouts, low-quality scans, and sometimes even handwritten notes that can throw a wrench into the smartest systems.
The trick is to anticipate these bumps in the road and build a workflow that's resilient enough to handle them. That’s what turns a frustrating experiment into a reliable business asset.
Handling Document Variations and OCR Issues
One of the first walls you'll hit is document variety. Your top ten vendors might send invoices that look completely different from one another, which makes a rigid, template-based system pretty useless. This is where AI-powered tools really prove their worth. They don't just look for data in a specific spot; they learn to identify it by context, finding an "Invoice Number" whether it's at the top left or bottom right.
Even with smart AI, bad document quality can still cause headaches for the Optical Character Recognition (OCR) engine. A fuzzy scan or a dark photo can easily make the system mistake a "B" for an "8."
Here’s how you can fight back:
- Improve Scan Quality: The cleaner the image, the better the result. Set a minimum standard for scans—I’ve found 300 DPI is a solid baseline—to give the OCR engine the best possible chance.
- Use Data Validation Rules: Build in simple checks to automatically flag fields that don't make sense. If a "Total Amount" field contains letters, that's an obvious error that can be kicked over for human review.
- Let the AI Use Context: Modern tools are great at this. They use surrounding data to guess the correct value, which dramatically boosts accuracy on documents that are far from perfect.
Great automation isn't about achieving 100% hands-off processing from day one. The real goal is to get to 95% automation and create an efficient, foolproof system for handling the remaining 5% of exceptions.
The Human-in-the-Loop Workflow
This brings me to one of the most practical concepts in automation: the human-in-the-loop system. Instead of chasing perfection, you set up your workflow to automatically flag anything it’s unsure about.
For example, if the software can't decipher a handwritten note or finds a mismatch between the line items and the total, it doesn't just guess. It pauses that specific document and routes it to a designated person for a quick manual check. You get the best of both worlds: incredible speed for most of your documents and human expertise for the tricky ones.
This approach ensures nothing slips through the cracks, and it’s absolutely essential when you first automate data entry. Over time, you can even use these manual corrections to retrain your AI model. This makes the system smarter with every document it processes, steadily reducing the number of exceptions. It’s a continuous feedback loop that turns your automation tool from a simple processor into an intelligent, evolving part of your team.
Common Questions About Automating Data Entry
When you're first looking into how to automate data entry, a few questions always pop up. Let's tackle the big ones I hear most often from people just starting out.
What's the Real Cost to Get Started?
The price tag for automation can swing wildly. For simpler needs, you can find template-based tools that start as low as $20-$50 a month. These are perfect if all your documents, like invoices from a key supplier, follow the exact same layout.
Once you get into more advanced AI or RPA software, you could be looking at a few hundred to several thousand dollars each month. The final cost really hinges on how many documents you process, how complex they are, and what other systems you need to connect to. The good news is that most services offer different pricing levels, so you can begin with a smaller plan and expand as your business grows.
Do I Need to Be a Tech Whiz to Set This Up?
Not like you used to. Today’s best data extraction platforms, including tools like DocParseMagic, are built for regular business users. Most have a simple, visual interface where you can point and click to show the software what data to pull. No coding required.
For a massive, company-wide rollout, you might want to loop in your IT team. But for most businesses, setting up and running your own data entry automation is completely doable without hiring a developer. These tools are designed for the people who actually handle the documents every day.
What About Messy, Handwritten Documents?
Yes, automation can handle handwriting—with a few asterisks. Modern OCR has evolved into what we call Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR), and it's surprisingly good at deciphering neat, block-style handwriting. Think of someone carefully filling out a standardized form.
But let's be realistic: cursive, sloppy, or rushed handwriting is still a tough nut to crack, even for the most advanced systems.
The best solution here is what's called a "human-in-the-loop" system. The software takes the first pass, extracts everything it's confident about, and then flags just the fuzzy, handwritten bits for a quick human check. It’s the perfect middle ground, giving you the speed of automation with the reliability of a human eye.
Tired of the copy-paste routine? See for yourself how simple it can be to turn messy documents into clean, usable data with DocParseMagic. Get started for free and see it in action.